Installing Script Plugins#
Scripts can either be installed manually, by dragging to the Avogadro window:
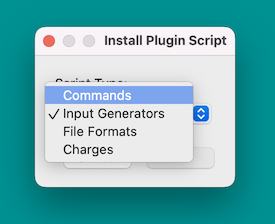
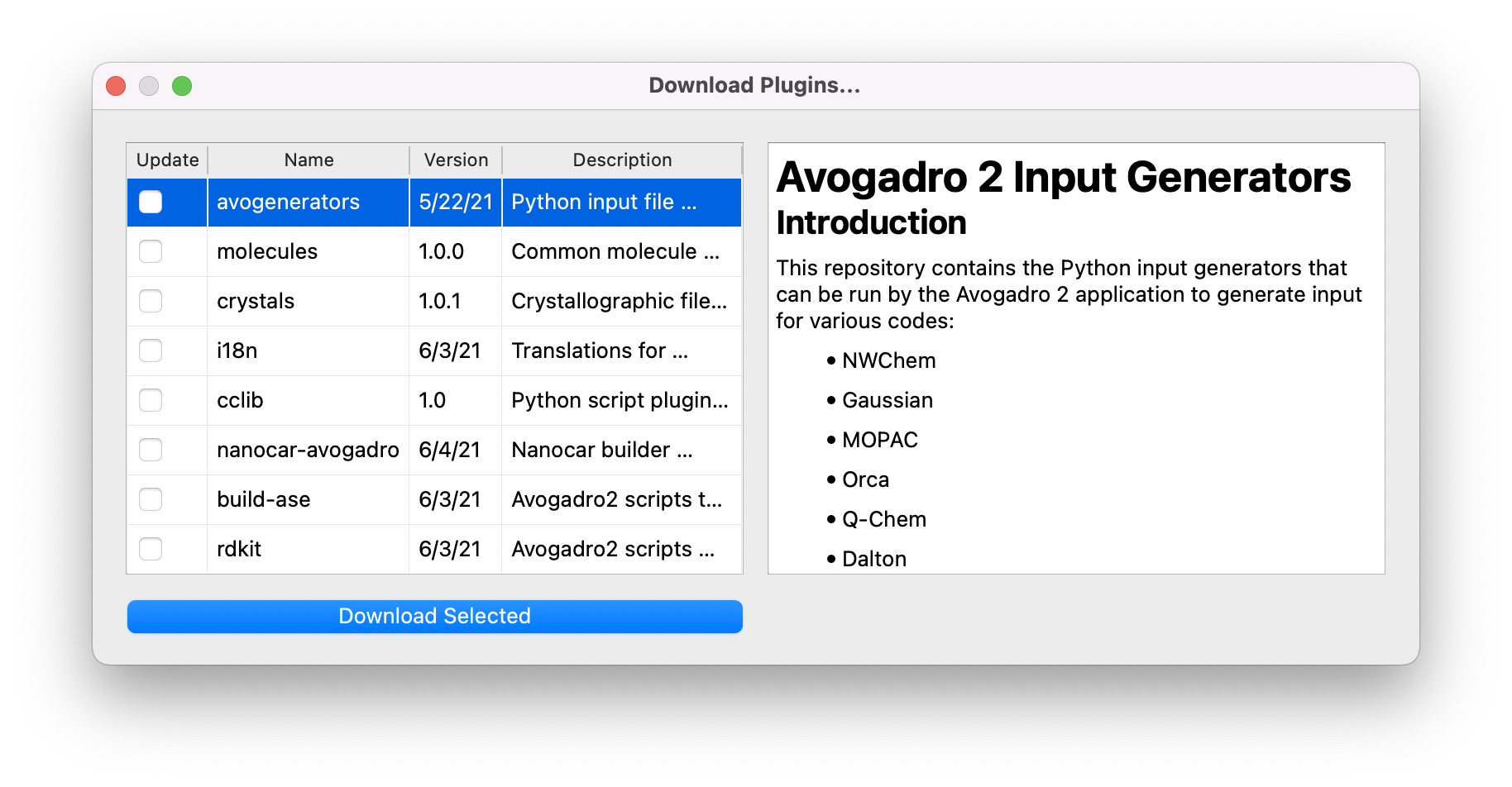
Scripts can also be installed from GitHub repositories through the “Download Plugins…” command:
Directories#
Avogadro will look for plugins either as individual files or subdirectories in a few different paths, including system and user directories.
User-installed plugins are found within the Avogadro data folder, the location
of which is determined by
QStandardPaths::standardLocations(QStandardPaths::AppLocalDataLocation):
Linux and BSD:
~/.local/share/OpenChemistry/AvogadromacOS:
~/Library/Application Support/OpenChemistry/AvogadroWindows:
C:/Users/<USER>/AppData/Local/OpenChemistry/Avogadro
Within this data folder, plugins are found in subdirectories organized by the category of plugin.
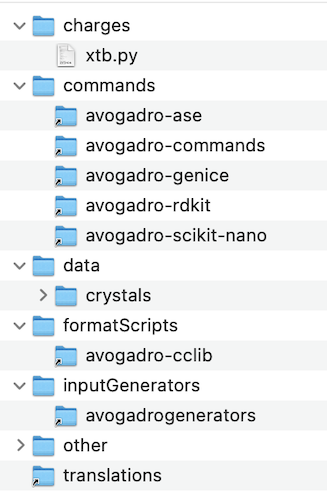
Current plugin categories and their respective subdirectories:
Scripts for calculating charges and electrostatic potentials – found in
chargesScripts to add menu options for commands, which perform custom operations – found in
commandsScripts that calculate energies and gradients on request by parts of Avogadro that run calculations – found in
energyScripts that generate input files for computational chemistry programs – found in
inputGeneratorsScripts that translate between different chemical file formats – found in
formatScripts
On startup, each of these subdirectories will be scanned for individual
plugin files, as well as plugin “packages” – directories containing mutliple
files as well as a plugin.json with information about the plugin.
Warning
The main data folder should not be used for plugin files and plugins saved there will not be loaded.
Plugins must be saved within the appropriate subdirectory for their type.
Plugin Packages and Repositories#
Since some plugins may require additional scripts or resources to function, they can be installed as entire self-contained directory to make a “package”.
avogadro-cclib - reads files through the
cclibPython module and needs autils.pyhelper scriptavogadro-rdkit - packages multiple command scripts together since they all use the
rdkitpackage
All repositories must include a plugin.json file, which is used by Avogadro
to indicate the actual plugin scripts (e.g., multiple commands)
as well as the Download Plugins… command to provide information to the user:
{
"author": "Geoffrey Hutchison",
"version": 1.0,
"url": "https://github.com/ghutchis/avogadro-scikit-nano",
"name": "avogadro-scikit-nano",
"description": "Generate carbon nanomaterial using scikit-nano",
"type": "commands",
"commands": [
{ "name": "SWNT", "command": "swnt.py" },
{ "name": "MWNT", "command": "mwnt.py" }
]
}
Required sections:
author: a user-visible attribution of the scriptversion: a version number of the script (which is ignored based on GitHub tags or releases)url: the URL of the GitHub repositoryname: the name of the plugin. Initialavogadro-prefix will be ignored by the Download Plugins… dialog.description: a brief description of the plugintype: the category of plugin script, including:chargesfor charge / electrostatics modelscommandsfor menu commandsenergyfor energy / force field modelsformatsfor file formatsgeneratorsfor input generators
commands: a list of key/value pairs to indicate a potentialnameand thecommandfilename for the script.
Note that any files not listed in the commands list will be ignored by
Avogadro during launch.
Adding to the Plugin Directory#
When you are ready to add your plugin repository to the download list, create a release and submit a pull request to: Avogadro/plugins
Someone will check your plugin and approve the addition to the list of approved repositories. An automated script runs daily to generate the cached information on the plugin repositories, so it may not appear immediately.
Suggestions for a more complete plugin repository system are welcome.
