Example Plugin Script - Part 1#
Let’s consider Alloy/Alchemy command as a reference for writing code for scripts or plugins
The Main function:#
The main function is responsible for parsing command-line arguments . It serves as the entry point for the script , facilitates its interaction with the user and executes the appropriate actions.
Below is a detailed explanation of the main function:
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser('Replace atoms of elements')
parser.add_argument('--debug', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--print-options', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--run-command', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--display-name', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--menu-path', action='store_true')
parser.add_argument('--lang', nargs='?', default='en')
args = vars(parser.parse_args())
debug = args['debug']
if args['display_name']:
print("Replace Elements")
if args['menu_path']:
print("&Build")
if args['print_options']:
print(json.dumps(getOptions()))
elif args['run_command']:
print(json.dumps(runCommand()))
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the main function:
Command-Line Argument Parsing: The
argparsemodule is used to define command-line arguments and parse them.Script Entry Points:
The script supports the following command-line arguments (Refer script entry points) :
--debug--print-options--run-command--display-name--menu-path--lang [language]
Debug Mode: If the
--debugflag is set, thedebugvariable is set toTrue. This can be used to control the script’s debugging behavior.
Input Arguments#
Display Name: If the
--display-nameflag is provided, the script printsReplace Elementsas the display name of the operation.Menu Path: If the
--menu-pathflag is provided, the script prints&Buildas the menu path where the operation can be found.Print Options: If the
--print-optionsflag is set, the script prints the available user UI options in JSON format using thegetOptionsfunction.Run Command: If the
--run-commandflag is set, the script executes therunCommandfunction, which performs the element replacement operation and returns the modified molecular structure in JSON format.
getOptions() Function#
def getOptions():
userOptions = {}
userOptions['Find'] = {}
userOptions['Find']['label'] = 'Find Element'
userOptions['Find']['type'] = 'stringList'
userOptions['Find']['values'] = list(element_dict.keys())
userOptions['Find']['default'] = "Carbon"
.....
return opts
The getOptions function is used to specify the script Interfaces or the pop-up menu for the script. For each option in the userOptions list, Avogadro will create appropriate labels, menus, text boxes, check boxes, etc. Interface will look something like this:
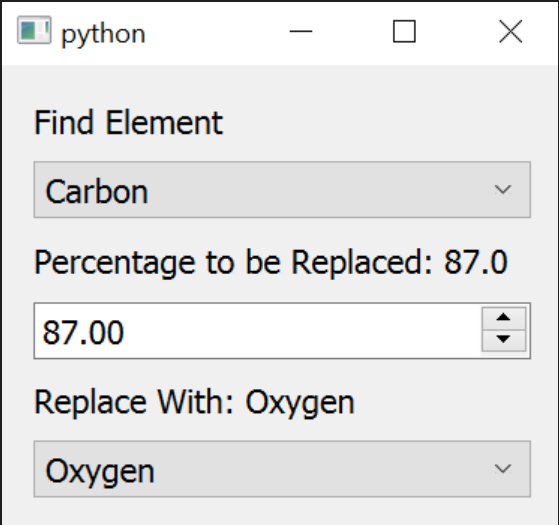
It is called in the command line when --print-options is given as the input argument.
