Acid-Base Properties of Amino Acids#
Investigate the pH-dependent protonation of amino acids.
Tasks#
Create and optimize the geometry of a glycine molecule (H2NCH2COOH). Open the “Build” menu and select “Add Hydrogens for pH…”. Choose different values of pH (1, 2, 3, …, 13) and note the effect of pH shift on the electrical charge of glycine.
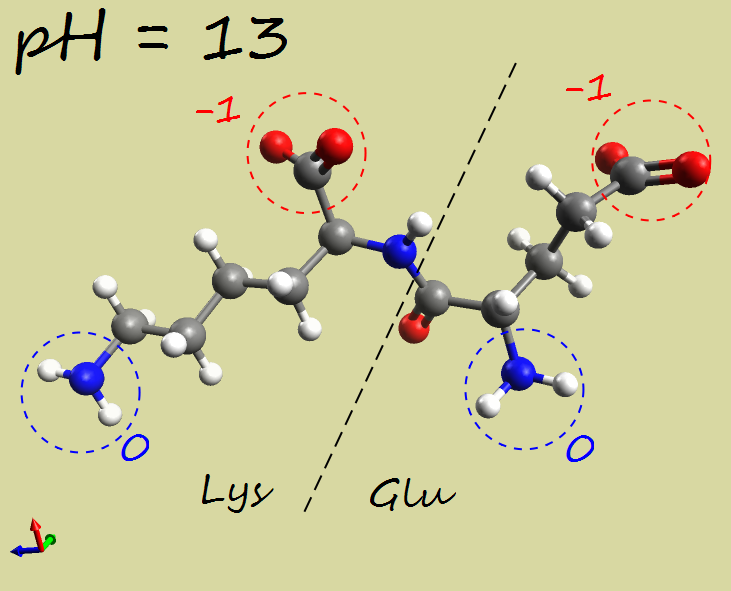
In a new View, create a (glutamic acid - lysine) dipeptide using the “Build” menu, then “Insert”, then “Peptides…”. Set the pH to 3 and calculate the corresponding electrical charge of the dipeptide. Do the same for pH 7 and pH 13.
When performing a paper electrophoresis at these pHs, in which direction will the dipeptide move (towards the anode or cathode)?
Solution#
Glycine electrical charge according to pH shift:
pH < 5: NH3+-CH2-COO-H+; net charge = +1.
5 ≤ pH < 10: NH3+-CH2-COO-; net charge = 0.
10 ≤ pH ≤ 13: NH2-CH2-COO-; net charge = -1.
Glu-Lys dipeptide:
pH |
|
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Net charge |
+1 |
-1 |
-2 |
Electrophoresis |
→ cathode (-) |
→ anode (+) |
→→ anode (+) |