Building Metal Complexes#
This tutorial demonstrates how to efficiently build coordination compounds and organometallic complexes using the Template Tool. We’ll progress from a simple complex to more sophisticated structures.
The Template Tool streamlines construction of metal complexes by providing pre-defined coordination geometries (octahedral, tetrahedral, square planar, etc.), a library of common ligands, and keyboard shortcuts for rapid building.
Activate the Template Tool with Ctrl+3 or by clicking its icon in the toolbar.
Part 1: A Simple Octahedral Complex#
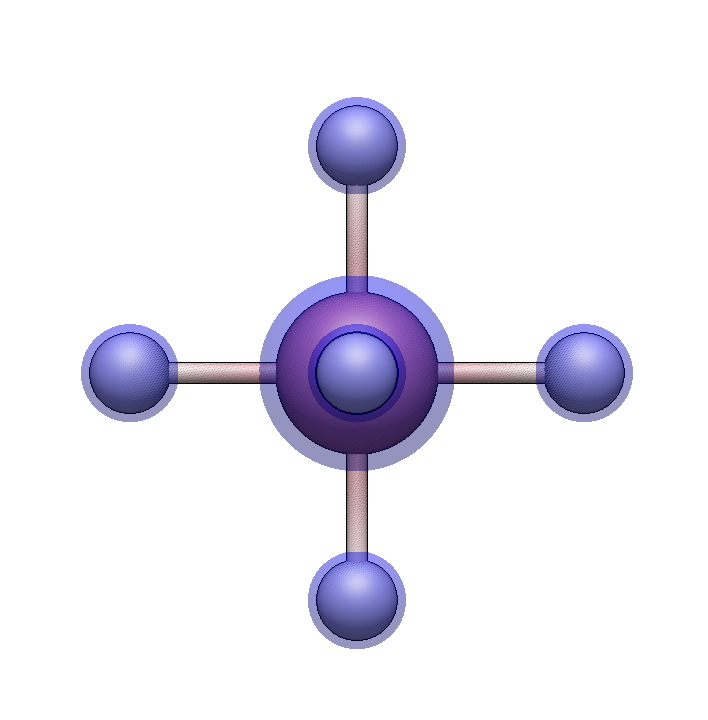
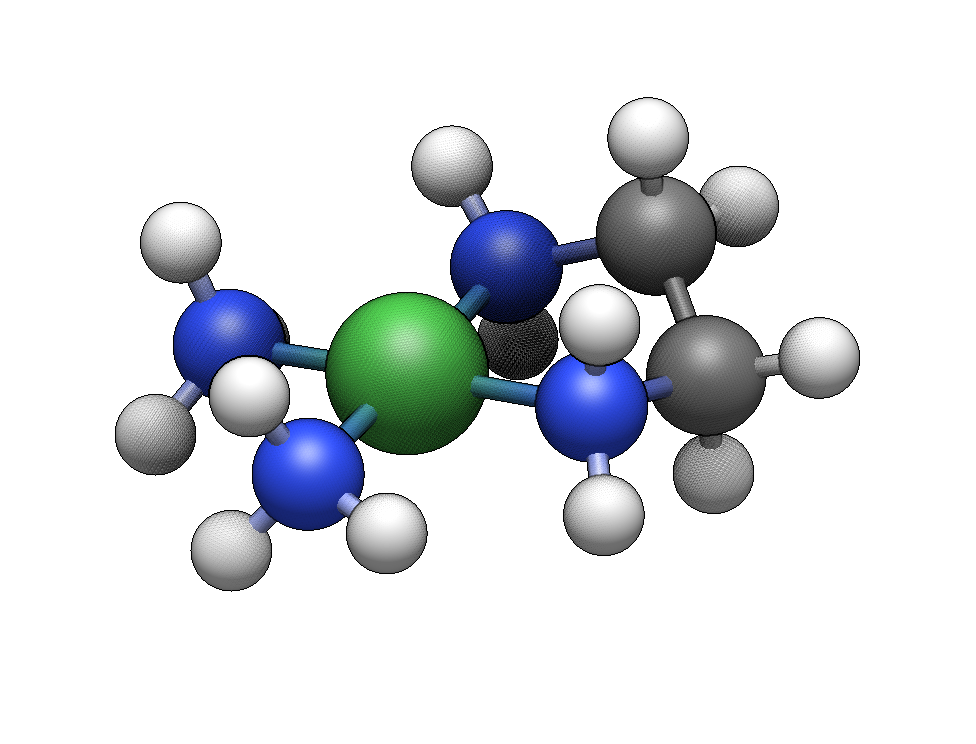
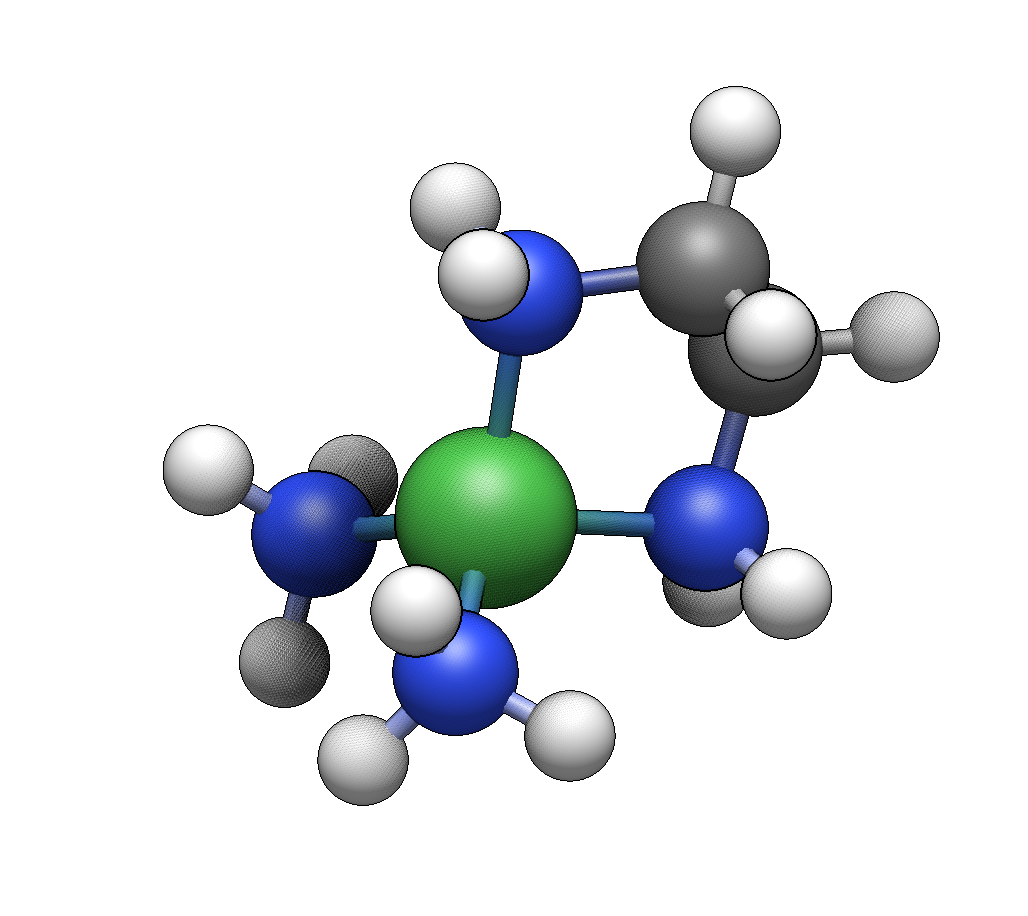
We’ll start by building [Co(NH₃)₆]³⁺, a classic Werner complex.
Set up the metal center
In the Centers tab, you can either use the options panel or some keyboard shortcuts:
Type
Coto select cobalt, or pick it from the popup menuPress + three times to set the formal charge to +3
Press 6 to select octahedral geometry
Click in empty space to place the cobalt center. Six hydrogen atoms will appear at the coordination sites.
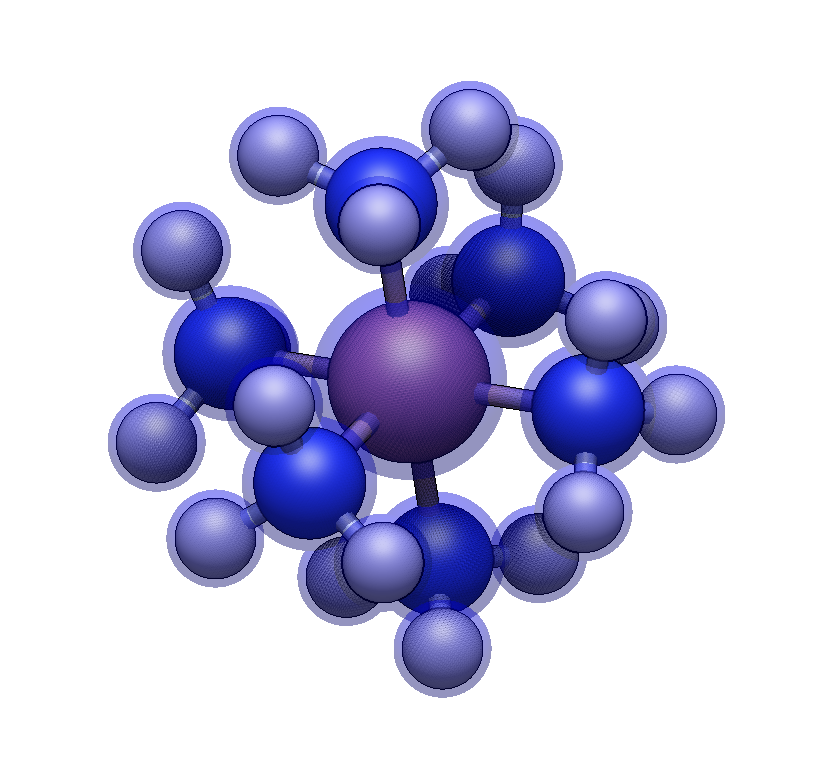
Add ammine ligands
Switch to the Ligands tab by pressing → or ] or clicking the tab:
Type
nto select ammine (NH₃)
Click on each of the six hydrogens. Each click replaces a hydrogen with an ammine ligand.
Other ligands can also be selected by keyboard shortcuts.
You now have a complete hexaamminecobalt(III) complex with idealized octahedral geometry.
Tip
For other simple complexes, change the element and ligand:
[Fe(CN)₆]⁴⁻: Use
Feand typecnfor cyano[Ni(CO)₄]: Use
Ni, tetrahedral (4), and typecofor carbonyl
Part 2: Mixed-Ligand Complex with Different Geometries#
Now we’ll build [Ni(en)(NH₃)₂]²⁺, which combines a bidentate ethylenediamine with two monodentate ammine ligands. We’ll also explore how the same ligand set can adopt different geometries.
Building the Square Planar Isomer#
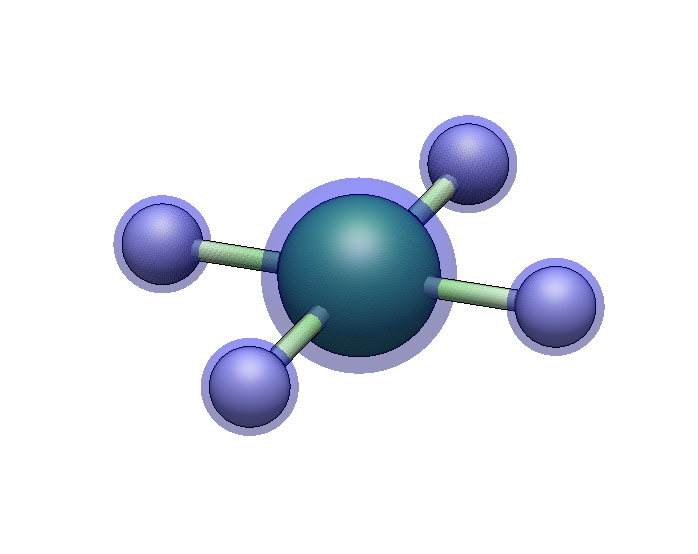
Create a square planar nickel center
In the Centers tab:
Type
Nito select nickelPress ++ for +2 charge
Press 44 for square planar geometry
Click to place the center.
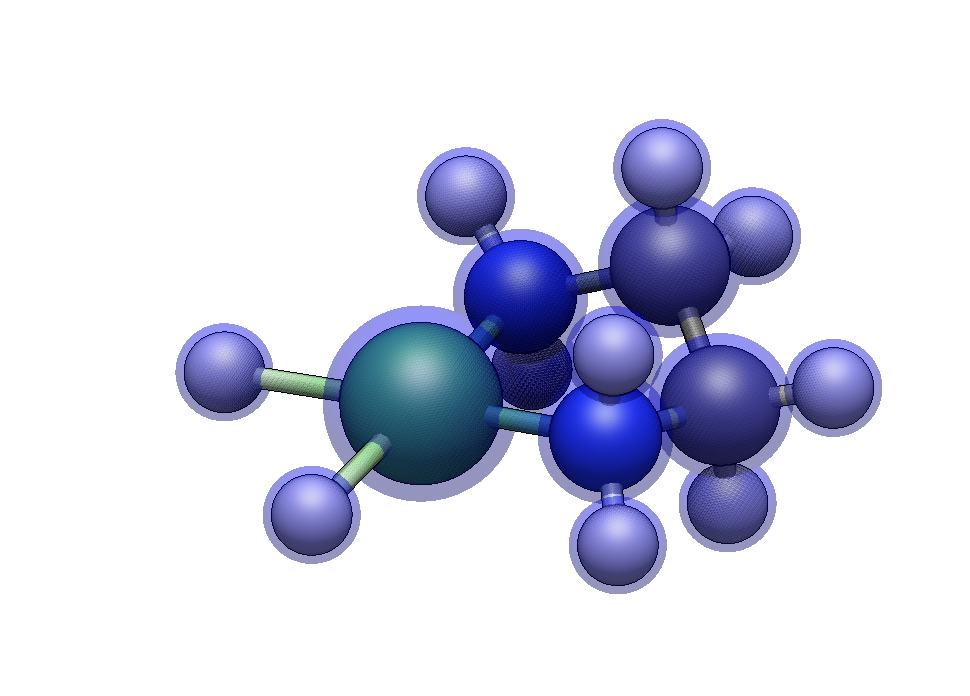
Add ethylenediamine
In the Ligands tab, type en to select ethylenediamine. Click on two adjacent hydrogen atoms (cis positions). The bidentate ligand bridges both sites, forming a five-membered chelate ring.
Add two ammine ligands
Type n for ammine, then click on each of the two remaining hydrogens.
Building the Tetrahedral Isomer#
Start fresh (File → New) and repeat with one change:
Press 4 (not 44) for tetrahedral geometry
Add the same ligands: ethylenediamine (en) to two adjacent hydrogens, then ammine (n) to the remaining two.
Note
Square planar and tetrahedral geometries are both common for d⁸ metals like Ni(II), Pd(II), and Pt(II). The preferred geometry depends on ligand field strength and steric factors. You can run quantum chemical calculations to compare the relative energies of the isomers.
Part 3: Organometallic Catalysts with Haptic Ligands#
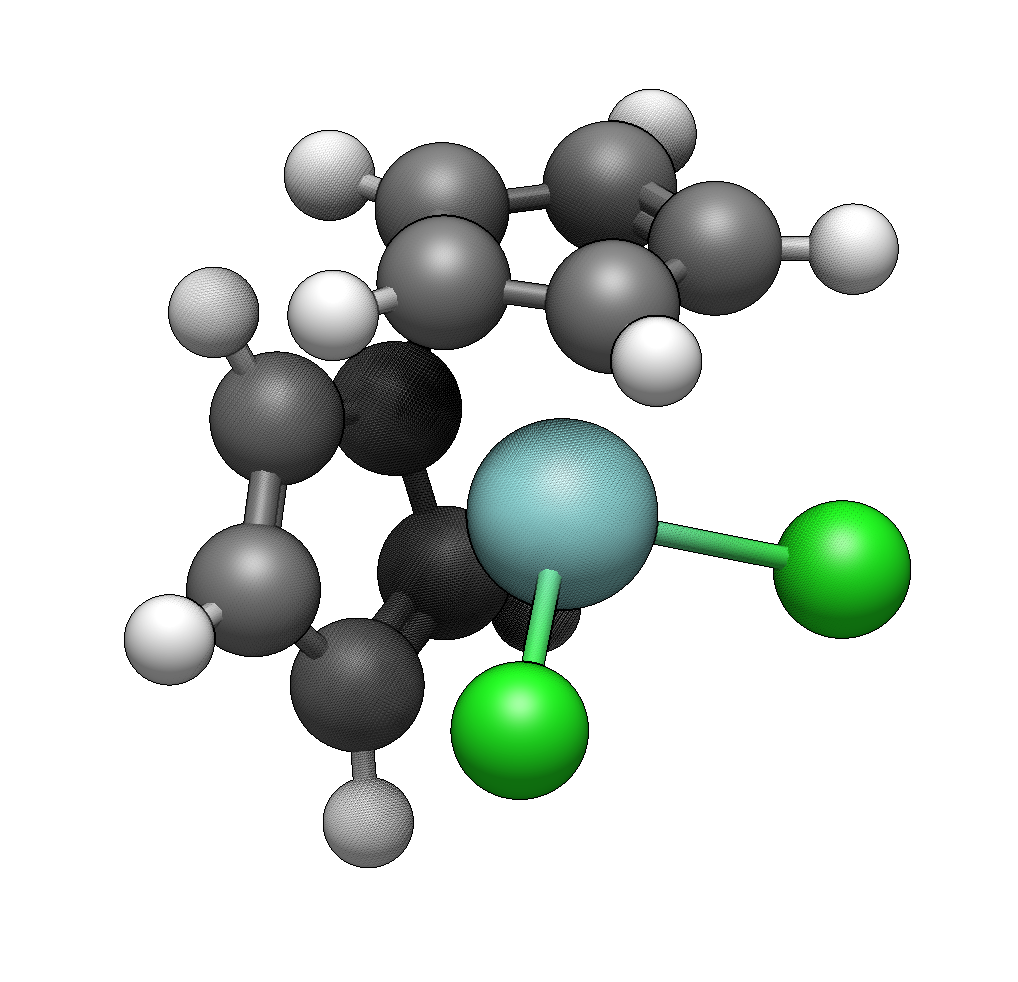
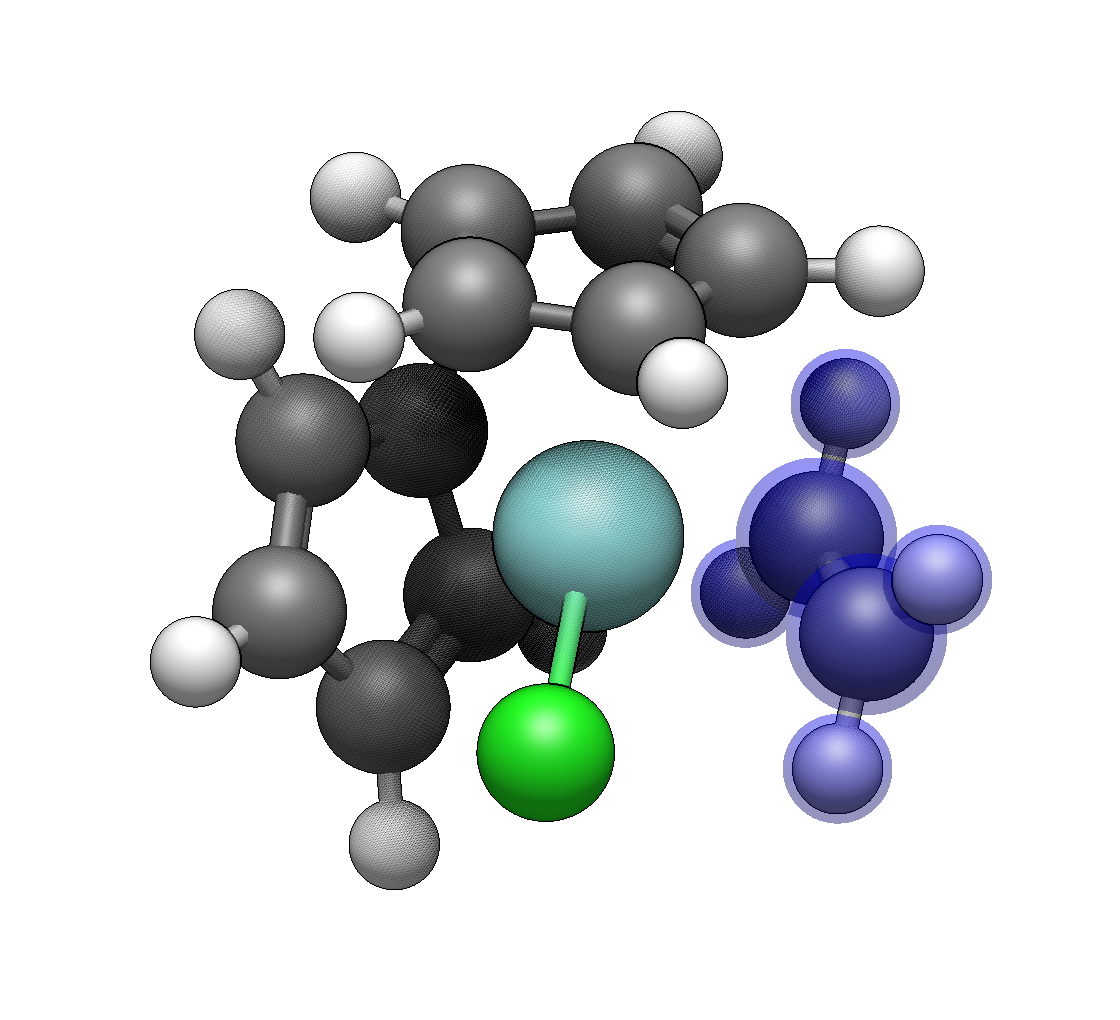
Finally, we’ll build a Ziegler-Natta type catalyst precursor: zirconocene dichloride (Cp₂ZrCl₂). This demonstrates haptic ligand attachment and mixed ligand types.
Zirconocene dichloride has a zirconium(IV) center with two η⁵-cyclopentadienyl (Cp) rings and two chloride ligands. The Cp rings bond through all five carbon atoms (haptic bonding), creating a bent metallocene structure.
Create the zirconium center
We need a 4-coordinate geometry, treating each Cp as occupying one site:
Type
Zrto select zirconiumPress + four times for +4 formal charge
Press 4 for tetrahedral geometry
Place the center.
Add the cyclopentadienyl rings
In the Ligands tab, type cp (or e5) to select η⁵-cyclopentadienyl.
Click on one hydrogen. The entire Cp ring attaches, with all five carbons oriented toward the metal. Click on an adjacent hydrogen to add the second Cp ring.
Add the chloride ligands
The Template Tool’s ligand library focuses on organic ligands. For chlorides, switch to the Draw Tool (Ctrl+2), select chlorine from the element selector, and click on each remaining hydrogen to replace it with Cl.
You could also type e2 to select η²-ethylene to insert in one site.
Tip
Try building related catalysts:
Titanocene dichloride: Use
Tiinstead ofZrHalf-sandwich complexes: Use only one Cp ring with other ligands
η⁶-arene complexes: Use
e6for benzene coordination
The ligand library also has other haptic coordination modes, such as a distorted η³-cyclopentadienyl for fluxional behavior.
Summary#
Complex Type |
Key Steps |
|---|---|
Simple octahedral |
Element → charge → 6 → place → add 6 monodentate ligands |
Mixed-ligand |
Element → charge → geometry → bidentate first → fill remaining sites |
Geometry comparison |
4 for tetrahedral, 44 for square planar |
Haptic complexes |
Use |
See Also#
Template Tool Reference for the complete list of keyboard shortcuts and options
Template Tool: Creating New Ligands for building custom ligands